Binary Tree Traversal
Tree traversal in an important data structure and can be applied in various data structures and algorithms. Here we will focus on binary tree and discuss the different traversal methods.
Traversal Methods
- Preorder Traversal : Root - Left - Right
- Inorder Traversal :Left - Root - Right
- Postorder Traversal :Left - Right - Root
- Level order Traversal: Breadth-First Search (BFS)
Preorder Traversal
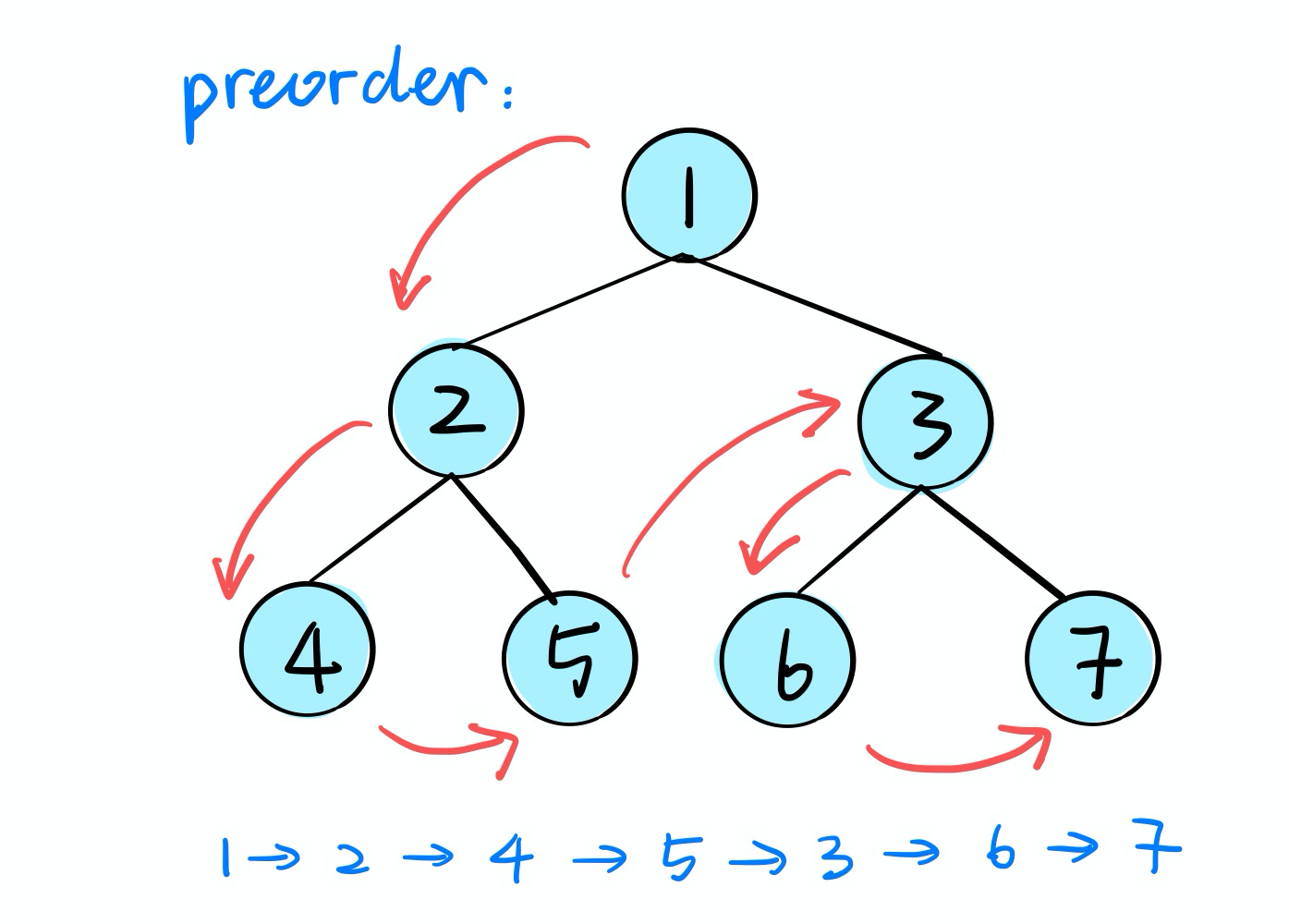
Algorithms:
1. Recursion:
class Solution:
def preorderRecur(self, root:TreeNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
def curr(root):
if not root:
return None
# in the order of root - left - right
res.append(root.val)
curr(root.left)
curr(root.right)
curr(root)
return res2. DFS(stack)
class Solution:
def preorderDFS(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
stack = []
if not root:
return res
stack.append(root)
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
res.append(node.val)
# push right first, pop left first
stack.append(node.right)
stack.append(node.left)
return resInorder Traversal
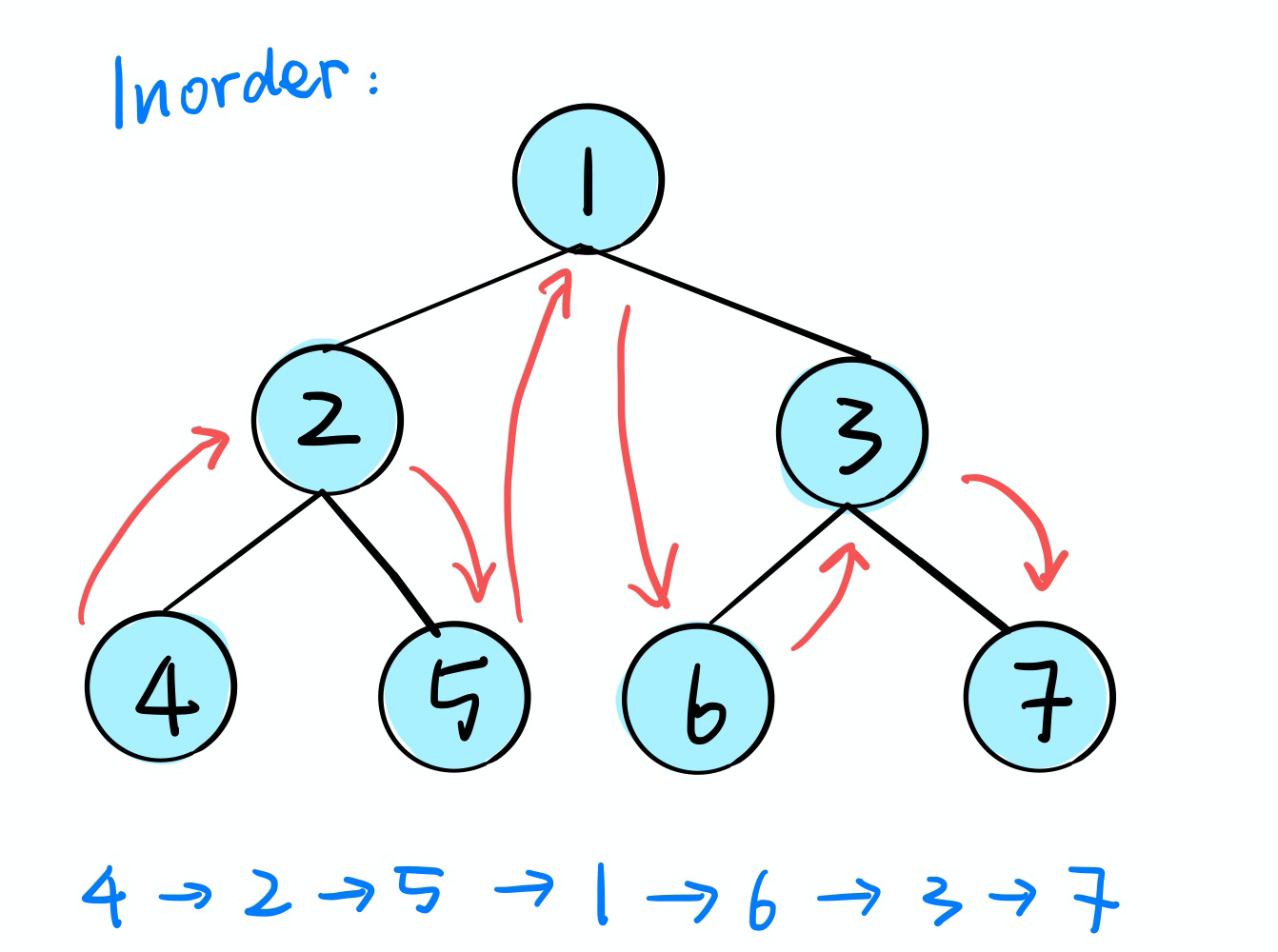
Algorithms:
1. Recursion:
class Solution:
def inorderRecur(self, root:TreeNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
def curr(root):
if not root:
return None
# in the order of left - root - right
curr(root.left)
res.append(root.val)
curr(root.right)
curr(root)
return res2. DFS(stack)
class Solution:
def inorderDFS(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
stack = []
while True:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
if not stack:
return res
root = stack.pop()
res.append(root.val)
root = root.right
return resPostorder Traversal
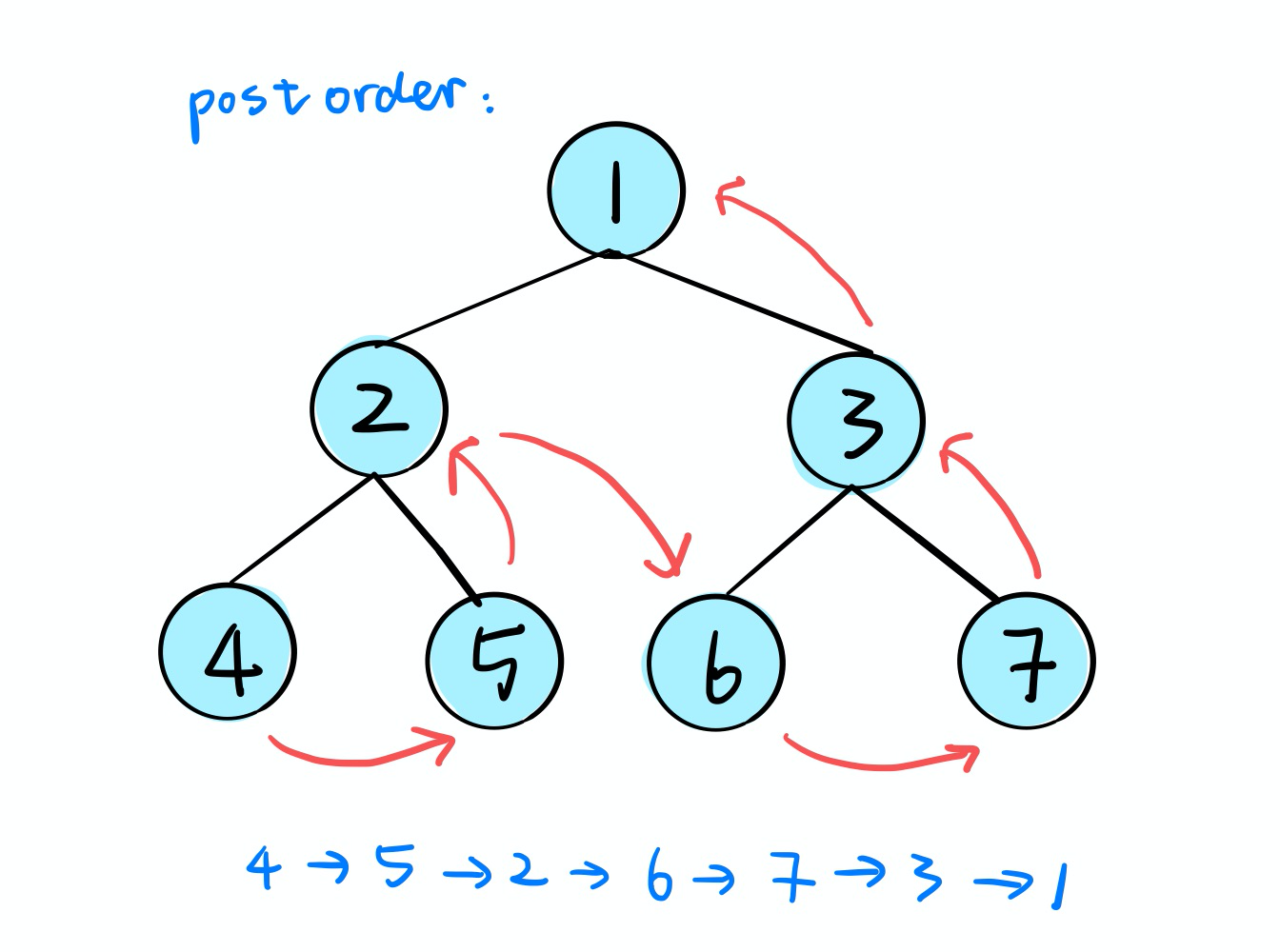
Algorithms:
1. Recursion:
class Solution:
def postorderRecur(self, root:TreeNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
def curr(root):
if not root:
return None
# in the order of left - right - root
curr(root.left)
curr(root.right)
res.append(root.val)
curr(root)
return res2. DFS(stack)
class Solution:
def postorderDFS(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
res = []
stack = []
if not root:
return res
stack.append(root)
while stack:
node = stack.pop()
if node:
res.append(node.val)
stack.append(node.left)
stack.append(node.right)
return res[::-1]Level Order Traversal
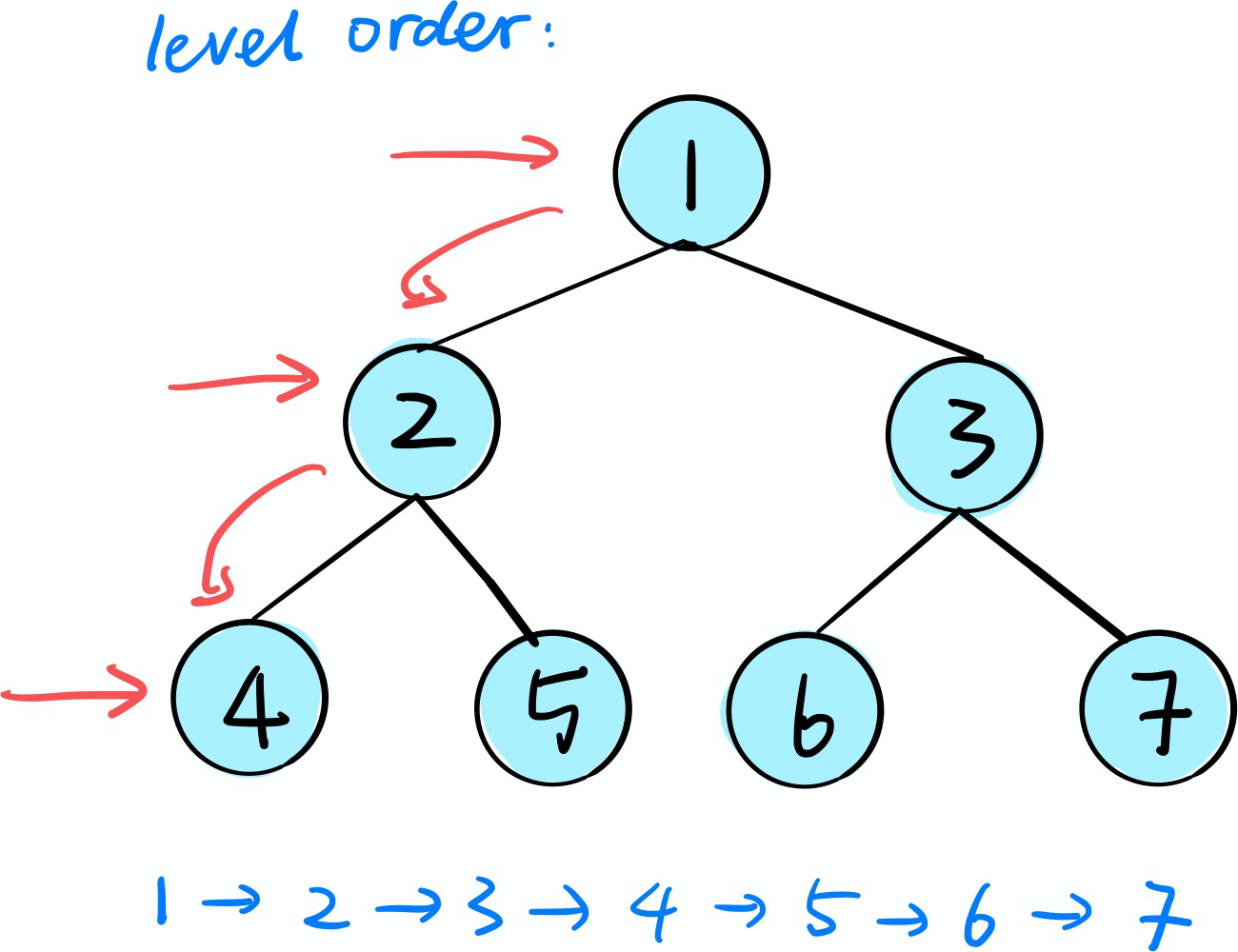
Algorithms: DFS(stack)
class Solution
def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[[int]]:
# if the tree is empty
if not root:
return []
result = []
level = deque()
level.append(root)
while level:
curr_level = []
# store the length of current level (unnecessary for python but needed for other language
a = len(level)
for _ in range(a): # traversal the current level
node = level.popleft()
curr_level.append(node.val)
if node.left:
level.append(node.left)
if node.right:
level.append(node.right)
result.append(curr_level)
return result