Binary Search
Binary Search is a powerful algorithm for allocating items in a sorted array. It efficiently reduce the size of a problem while solving it, with two pointers used to reduce the searching area. Binary Search is also widely applied in daily life, such as Price Guessing Game.
Binary Search vs. Linear Search
| Binary Search | Linear Search | |
|---|---|---|
| Worst case time complexity | O(logN) | O(N) |
| Array type | Sorted | No Need to be Sorted |
Binary Search Methods
Template 1: Searching for Existing Element
Known the target element is in the array, search its position.
Description
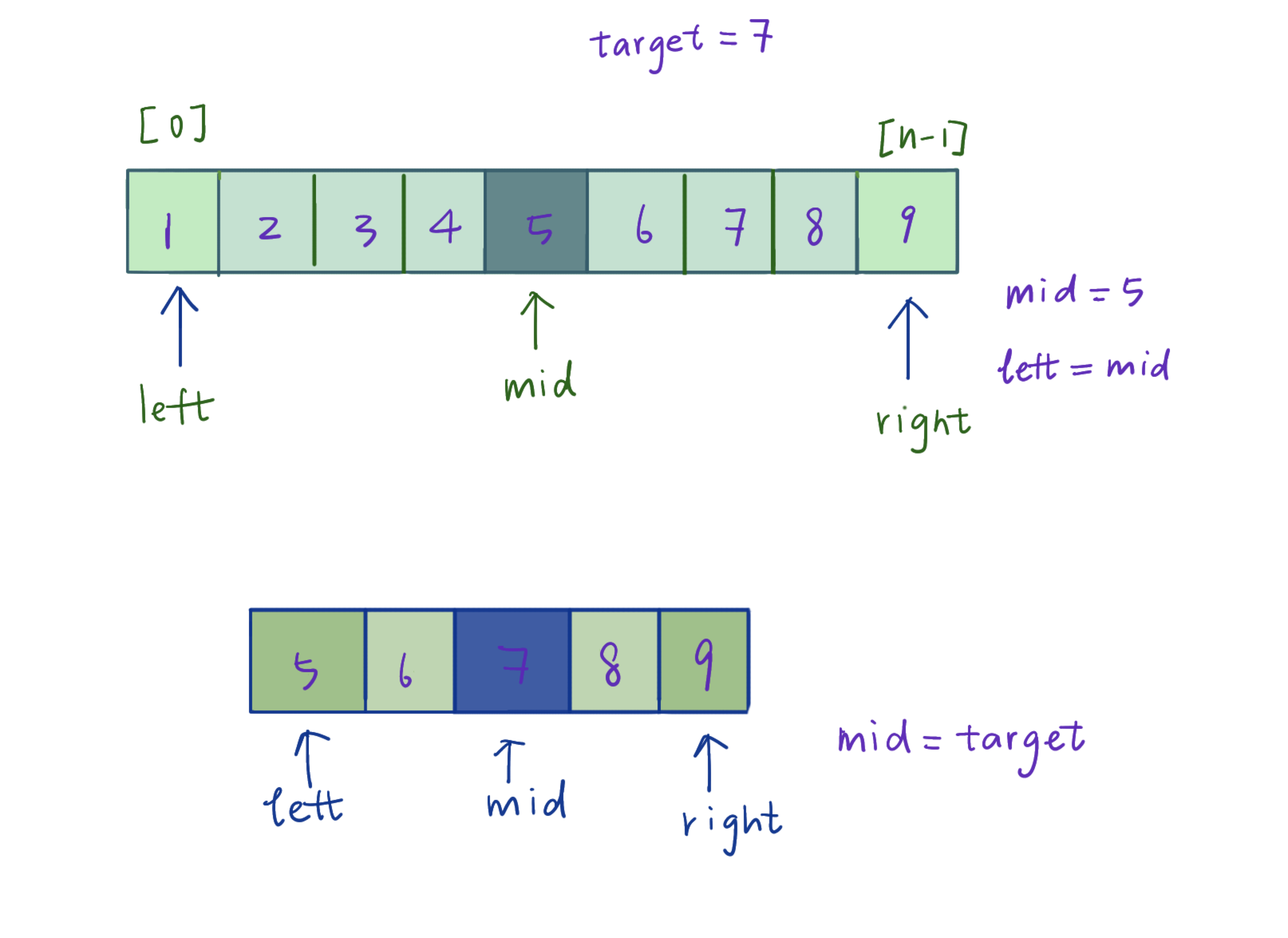
- Set up pointers
leftandright - Find the middle element
mid- If
midequals target element, return directly. - if
midis lower than target, setleftasmidand research its right side. - if
midis higher than target, setrightasmidand research its left side.
- If
Example
def search(nums: [int], target: int) -> int:
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
#including the search when left == right
while left <= right:
# take left-mid
"""important:to avoid (left + right) overflow from the range of numbers"""
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
elif nums[mid] < target:
# search area [mid+1, right]
left = mid + 1
else:
# search area [left, mid - 1]
right = mid - 1
return -1Notes
while left <= right: need to search one more time whenleft == rightmid = left + (right - left) // 2floors division to the left. Depending on question requirement, ceiling to the right can be simply done by adding 1.
Template 2: Searching for inserting place of element not in the array
Searching for the postion to insert the new element without breaking the order of the array.
Description
Set up pointers
leftandrightNeed to pay attention to the value on the boarder, otherwise may excluding the element and return error.
Find the middle element
midand comparemidwith target- if
midis lower than target, setleftasmid + 1and research its right side. - if
midis higher than target, setrightasmidand research its left side.
- if
Example
Leetcode 0035 - Search Insert Position
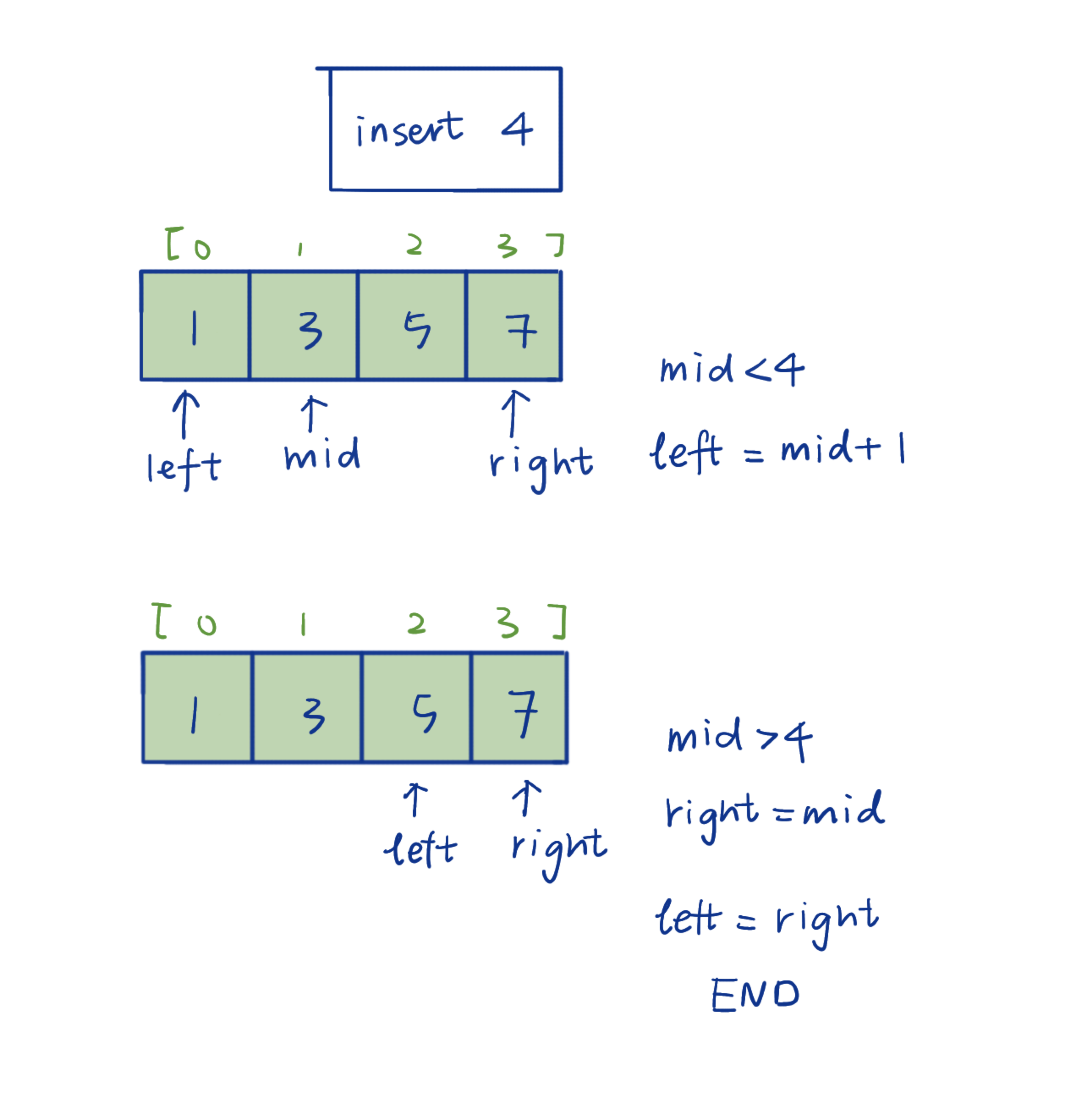
def searchInsert(nums: [int], target: int) -> int:
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left < right:
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
if nums[mid] > target:
right = mid
else:
left = mid + 1
# find the place to insert if target not in the list
if nums[left] < target:
return left + 1
else:
return leftImportant: Avoid dead loop
While reducing the area, whether floor or ceiling mid is very important in terms of avoiding dead loop
midbelongs to the left and divides the searching area into two parts:[left, mid]and[mid + 1, right], then for next round of search, the area would need to be# floor mid mid = left + (right - left) // 2 if check(mid): left = mid + 1 else: right = midmidbelongs to the right and divides the searching area into two parts:[left, mid - 1]and[mid, right]#ceiling mid mid = left + (right - left) // 2 + 1 if check(mid): left = mid else: right = mid - 1
Note: print out left, mid and righ is very helpful for debugging
Leetcode Practice Questions (to be added)
Search required position
Search for required answer in a given range
Matrix (multi-dimensions)
Useful Library
python
bisect: Bisect library allows direct use of bisection. Detailed usage and examples are well documented.
C++
iterator lower_bound( const key_type &key ): return the position of the first element <= target
iterator upper_bound( const key_type &key ): return the position of the first element >= target